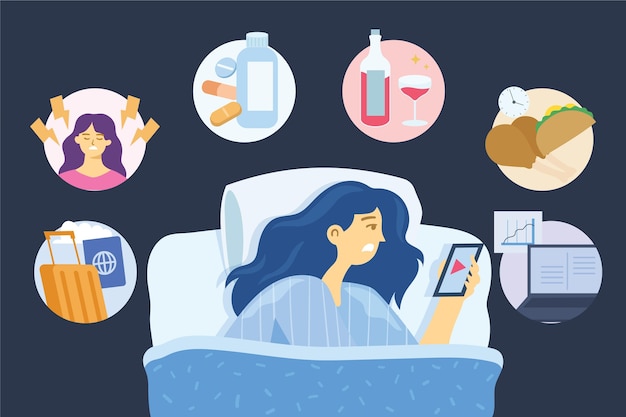


Some medicines have a stimulating effect, causing wakefulness and alertness. Stopping medicine that encourages sleep after long-term use can lead to severe insomnia. Medications can be a major cause of insomnia.

#Other possible causes for severe insomnia how to#
How to Cope with InsominaĪddress these environmental factors to improve your sleep. Other disruptive environmental factors include concerns about safety in the house, caring for a family member or a rapid ascent to a high altitude. A snoring sleep partner or an uncomfortable bed can also disturb sleep. Loud noise, bad odors, bright lights and extremes in room temperature can disturb sleep. Keep a regular bedtime routine and schedule, even on days off from school. Identify and deal with attempts to delay bedtime by limiting activity before bed so sleep can occur naturally and quickly.Įliminate stimulating activities close to bedtime. Some children are unable to sleep unless a special blanket or pacifier is present. These include fear of the dark, fear of being left alone or an unreasonably early bedtime. However, several other factors may also affect a child's sleep. Once this is accomplished, sleep often occurs naturally and quickly. These attempts to delay the bedtime should be recognized by the caretaker and then limited before bedtime.
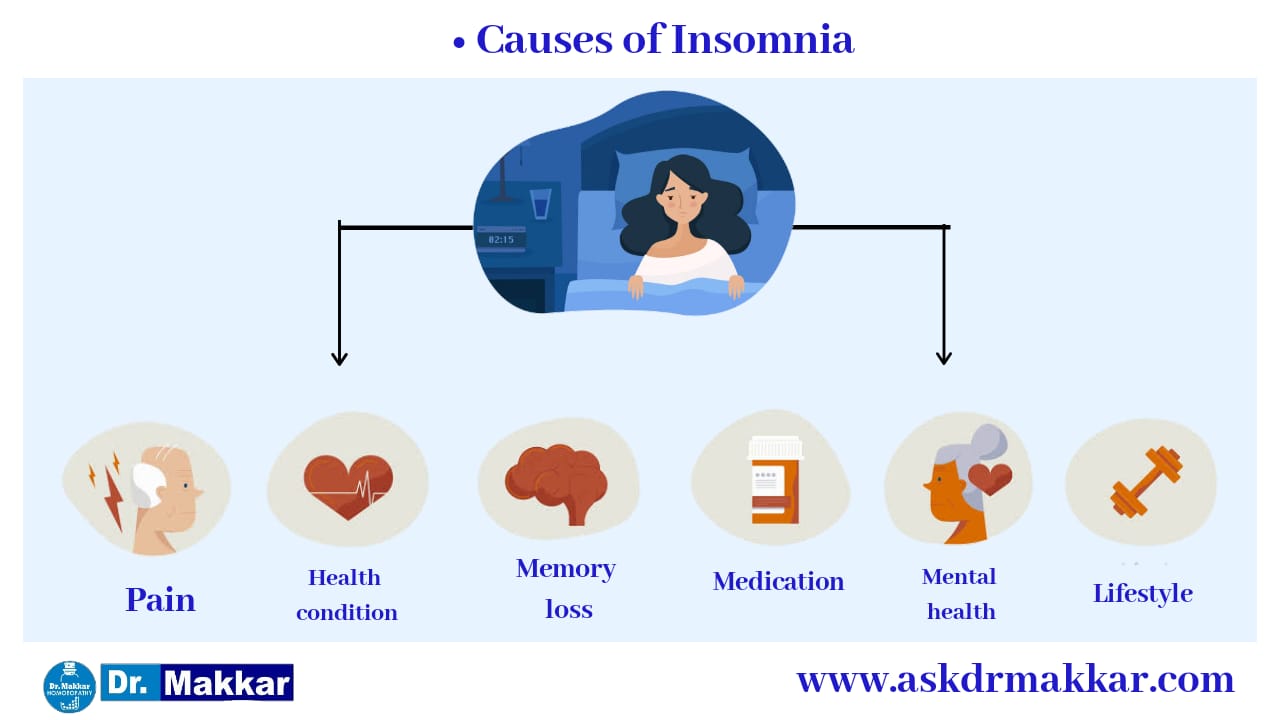
A child may ask for one more bedtime story, take several trips to the bathroom, ask for food or water or ask to watch a few more minutes of television. Meditate on positive and pleasant thoughts or topics to redirect thoughts.Ĭhildren often attempt to delay bedtime. Tense then relax each muscle group to help your muscles relax. Sleep tends to return to normal once the stress is removed or reduced or when the person learns to cope with it. Sleeping in new settings such as a hotel or hospital room can also lead to insomnia. Acute stress, such as major life events (tragic loss, marriage, a job change or an exam) can lead to insomnia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
